Everyone faces tough times, but not everyone bounces back stronger. Research from Harvard shows that resilience is not some rare trait only a few people have—it’s a set of skills anyone can build over time. Most people think resilience is about staying tough or ignoring stress, yet the real secret is that personal growth often happens right in the middle of adversity. Keep reading for the best resilience building exercises to keep you sharp.
Table of Contents: Resilience Building Exercises
- Understand Resilience And Its Importance
- Practice Mindfulness And Meditation Techniques
- Set Achievable Goals For Personal Development
- Engage In Positive Self-Talk And Affirmations
- Build A Strong Support Network
- Learn Problem-Solving Skills Through Challenges
- Reflect On Experiences To Foster Growth
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Resilience is a learnable skill. | Resilience can be developed over time through supportive relationships and personal capabilities, rather than being a fixed trait. |
| Practice mindfulness and meditate regularly. | Mindfulness and meditation techniques enhance emotional awareness, reduce anxiety, and improve stress response mechanisms when practiced consistently. |
| Set SMART goals for personal growth. | Establishing Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound goals helps create actionable steps for personal development and fosters resilience. |
| Engage in positive self-talk. | Transforming internal dialogue from self-critical to supportive enhances emotional responses and overall mental well-being, boosting resilience. |
| Build a robust support network. | Cultivating strong relationships provides essential emotional, instrumental, and informational support, enhancing your resilience during difficult situations. |
1: Understand Resilience and Its Importance
Resilience represents the extraordinary human capacity to bounce back from challenges, adapt to adverse circumstances, and grow stronger through difficult experiences. At its core, resilience is not about avoiding stress or preventing challenges but developing the psychological and emotional tools to navigate them effectively.
According to Harvard Graduate School of Education, resilience is a positive, adaptive response that emerges through supportive relationships and personal capabilities. This means resilience is not a fixed trait but a skill that can be cultivated and strengthened over time.
Key aspects of resilience include:
Emotional regulation: Managing stress and emotional responses effectively
Positive perspective: Maintaining hope and optimism during challenging situations
Problem solving: Developing adaptive strategies to overcome obstacles
Social connection: Building and maintaining supportive relationships
Understanding resilience requires recognizing that it involves more than just enduring hardship. It encompasses recovering from setbacks, maintaining functionality under pressure, and experiencing personal growth through challenges. People with high resilience do not simply survive difficult circumstances they emerge transformed, with enhanced emotional strength and improved coping mechanisms.
Resilient individuals demonstrate remarkable psychological flexibility. They view challenges as opportunities for learning and personal development rather than insurmountable barriers. This mindset allows them to reframe negative experiences, extract valuable insights, and continuously evolve their approach to life’s complexities.
By comprehending resilience as a dynamic, learnable skill, individuals can actively invest in developing their mental and emotional resources. The journey of building resilience is personal, nonlinear, and profoundly empowering, offering a pathway to navigate life’s uncertainties with greater confidence and adaptability.

2: Practice Mindfulness and Meditation Techniques
Mindfulness and meditation represent powerful techniques for building resilience by training the mind to respond to stress with clarity, calmness, and intentionality. These practices enable individuals to develop greater emotional awareness, reduce reactive behaviors, and cultivate inner stability in challenging situations.
According to research published in a neurological study, meditation interventions can create significant neurological changes that enhance an individual’s capacity for resilience. These practices rewire neural pathways, promoting more adaptive responses to stress and emotional challenges.
Key meditation techniques for building resilience include:
Breath awareness: Focusing attention on breathing patterns to anchor oneself in the present moment
Body scan meditation: Systematically relaxing different body parts to release physical tension
Loving kindness meditation: Cultivating compassion for oneself and others
Mindful observation: Practicing non judgmental awareness of thoughts and emotions
Consistent meditation practice transforms how the brain processes stress. Regular engagement helps individuals develop emotional regulation skills, reduce anxiety, and increase overall psychological flexibility. By training the mind to observe thoughts without becoming entangled in them, practitioners learn to create space between emotional triggers and their responses.
Mindfulness techniques go beyond traditional seated meditation. They can be integrated into daily activities like walking, eating, or working. The goal is developing a continuous state of present moment awareness that allows for more deliberate and thoughtful interactions with challenging experiences.
Practitioners should approach mindfulness with patience and self compassion. Progress is not about achieving a perfect meditative state but about consistently showing up and developing a non judgmental relationship with one’s inner experiences. Even short daily practices of 5 to 10 minutes can yield significant improvements in emotional resilience and mental clarity.
3: Set Achievable Goals for Personal Development
Personal development through strategic goal setting is a fundamental approach to building resilience and creating meaningful life progress. Goals serve as navigational tools that transform abstract aspirations into concrete, actionable plans, providing direction and motivation during challenging times.
According to Ohio University’s WellWorks program, establishing SMART goals is crucial for effective personal development. SMART is an acronym representing key goal characteristics:
Specific: Clearly defined objectives with precise outcomes
Measurable: Quantifiable indicators to track progress
Achievable: Realistic targets within your current capabilities
Relevant: Goals aligned with broader personal values
Time-bound: Defined timelines for completion
Effective goal setting requires a balanced approach that challenges personal limits while maintaining psychological safety. This means creating objectives that stretch your capabilities without overwhelming your current resources and emotional capacity. The process involves understanding your current strengths, identifying areas for growth, and designing incremental steps towards meaningful transformation.
Psychological research suggests that breaking larger goals into smaller, manageable milestones increases motivation and reduces feelings of being overwhelmed. For instance, if your ultimate goal is professional advancement, you might create intermediate objectives like completing an online course, networking with three professionals monthly, or developing a specific skill set.
Resilience emerges through the goal setting process itself. Each small achievement builds confidence, while setbacks become opportunities for learning and recalibration. The key is maintaining a flexible mindset that views goals as dynamic roadmaps rather than rigid mandates.
Successful goal setting also involves regular self reflection and adjustment. Periodically reassess your objectives, celebrate progress, and be willing to modify your approach based on new insights or changing circumstances. This adaptive strategy ensures continuous personal growth and maintains motivation during challenging periods.

4: Engage in Positive Self-Talk and Affirmations
Positive self-talk represents a powerful psychological strategy for building resilience, transforming internal narratives from self-critical to constructive and supportive. By consciously reshaping our inner dialogue, we can significantly influence our emotional responses, cognitive processing, and overall mental well-being.
According to research published in Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, self-affirmation activates brain regions associated with self-related processing and reward, demonstrating the neurological impact of positive self-communication.
Effective positive self-talk strategies include:
Reframing negative thoughts: Converting self-defeating statements into constructive perspectives
Using compassionate language: Speaking to yourself with the same kindness you would offer a close friend
Acknowledging effort over outcome: Celebrating personal growth and attempting challenges
Practicing present moment validation: Recognizing current strengths and capabilities
Resilience emerges through consistent internal dialogue that acknowledges challenges without being overwhelmed by them. This approach involves recognizing difficult emotions while simultaneously maintaining a perspective of personal capability and potential growth. When confronting setbacks, resilient individuals use self-talk that emphasizes learning, adaptability, and forward momentum.
Affirmations work most effectively when they are specific, personal, and grounded in realistic self-perception. Generic, overly positive statements can feel disconnected and insincere. Instead, craft affirmations that genuinely resonate with your experiences, values, and aspirations.
Incorporating positive self-talk requires deliberate practice. Start by observing your current internal dialogue, identifying patterns of self-criticism, and consciously replacing them with more supportive, encouraging statements. This is not about toxic positivity but about developing a balanced, compassionate relationship with yourself.
Remember that building resilient self-talk is a skill. Like any skill, it improves with consistent practice, patience, and self-compassion. Your internal narrative has the power to shape your experiences, emotional responses, and ultimately, your capacity to navigate life’s challenges with strength and grace.
5: Build a Strong Support Network
A robust support network serves as a critical foundation for resilience, providing emotional sustenance, practical assistance, and collective strength during challenging life experiences. Social connections are not merely a luxury but a fundamental psychological resource that enhances our ability to navigate adversity.
According to the RAND Corporation’s research on social fitness, social support encompasses three essential dimensions that contribute to individual resilience:
Emotional support: Offering empathy, care, and understanding during difficult times
Instrumental support: Providing tangible assistance like practical help or resources
Informational support: Sharing advice, guidance, and helpful perspectives
Building a diverse and reliable support network requires intentional effort and genuine relationship cultivation. This means developing connections across different domains of life, including family, friends, professional colleagues, mentors, and community groups. Quality matters more than quantity, emphasizing deep, authentic relationships over superficial interactions.
Effective networking involves mutual vulnerability and reciprocity. Being willing to both give and receive support creates a dynamic ecosystem of emotional resilience. This means being open about your challenges, actively listening to others, and demonstrating genuine care and commitment to your relationships.
Strategies for expanding and strengthening your support network include participating in community groups, joining professional associations, attending workshops, and leveraging social platforms that facilitate meaningful connections. The goal is creating a supportive ecosystem that provides different perspectives, emotional resources, and collaborative opportunities.
Resilience emerges through these interconnected relationships. When individuals feel supported, they develop greater confidence in their ability to overcome challenges. Your support network becomes a collective resource, offering different strengths, experiences, and insights that help you navigate life’s complexities with greater adaptability and emotional fortitude.
6: Learn Problem-Solving Skills Through Challenges
Problem-solving skills represent a critical mechanism for building resilience, transforming challenges from overwhelming obstacles into opportunities for growth and learning. By developing systematic approaches to navigating complex situations, individuals can enhance their capacity to manage stress, adapt to change, and emerge stronger from difficult experiences.
According to a randomized controlled trial with nursing students, targeted problem-solving skills training can significantly increase resilience and reduce perceived stress levels across various professional and personal contexts.
Key components of effective problem-solving for resilience include:
Systematic analysis: Breaking complex problems into manageable components
Emotional regulation: Managing stress and anxiety during challenging situations
Creative thinking: Generating multiple potential solutions
Adaptive flexibility: Willingness to modify approaches based on new information
Resilient problem-solving involves viewing challenges as dynamic puzzles rather than insurmountable barriers. This approach requires developing a mindset that sees difficulty as an opportunity for learning and personal development. Instead of becoming overwhelmed, resilient individuals approach problems with curiosity, intentionality, and a belief in their capacity to navigate complexity.
The process begins with objective assessment. This means stepping back from emotional reactivity to analyze the situation comprehensively. Consider gathering relevant information, identifying potential resources, and understanding the broader context of the challenge.
Practical problem-solving also demands emotional intelligence. Recognize your initial emotional responses without being controlled by them. Create mental space between the challenge and your reaction, allowing for more strategic and thoughtful engagement.
Cultivating problem-solving skills is an ongoing journey. Each challenge becomes a training ground for developing greater psychological flexibility, emotional maturity, and confidence in your ability to navigate life’s uncertainties. By consistently approaching problems as opportunities for growth, you transform potential sources of stress into powerful mechanisms for personal development.

7: Reflect on Experiences to Foster Growth
Reflective practice serves as a powerful catalyst for personal growth and resilience, transforming raw experiences into profound learning opportunities. By intentionally examining our experiences with curiosity and openness, we develop deeper self-understanding and create pathways for continuous personal development.
According to Cornell Health’s resilience research, cultivating a growth mindset through reflection enables individuals to view challenges as opportunities for learning and transformation.
Key strategies for meaningful reflection include:
Journaling: Recording experiences, emotions, and insights systematically
Structured questioning: Asking reflective questions about challenges and personal responses
Emotional mapping: Tracking emotional patterns and triggers
Learning extraction: Identifying specific lessons from challenging experiences
Effective reflection transcends mere recollection. It involves critically analyzing experiences, understanding personal responses, and consciously developing strategies for future growth. This process requires emotional honesty, vulnerability, and a commitment to continuous learning.
The reflection process demands non judgmental observation. Instead of criticizing past actions, approach your experiences with compassionate curiosity. Recognize that every experience provides valuable information about your strengths, limitations, and potential for growth.
Resilience emerges through this deliberate practice of turning experiences into wisdom. By consistently reflecting on challenges, setbacks, and successes, you develop a more nuanced understanding of your capabilities. This self awareness becomes a powerful tool for navigating future uncertainties with greater confidence and adaptability.
Remember that reflection is a skill that improves with practice. Start small by dedicating brief, consistent periods for introspection. Whether through journaling, meditation, or structured conversations, create space for honest self examination. Each moment of reflection is an investment in your personal growth and resilience.
Below is a comprehensive table summarizing the main exercises, key approaches, and outcomes discussed in the article for building resilience and fostering personal growth.
| Exercise / Strategy | Core Approach | Key Outcomes / Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Understand Resilience and Its Importance | Recognize resilience as a learned skill vs. fixed trait | Greater adaptability, personal growth, improved stress coping |
| Practice Mindfulness and Meditation Techniques | Use breathwork, body scans, mindful observation, loving kindness | Enhanced emotional regulation, reduced anxiety, present focus |
| Set Achievable Goals for Personal Development | Establish SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals | Direction, motivation, incremental progress, confidence |
| Engage in Positive Self-Talk and Affirmations | Reframe negative thoughts, practice self-compassion, validate efforts | Improved self-esteem, emotional resilience, constructive mindset |
| Build a Strong Support Network | Cultivate diverse, supportive relationships intentionally | Emotional, practical, and informational support resources |
| Learn Problem-Solving Skills Through Challenges | Systematic problem analysis, flexible and creative thinking | Reduced stress, skillful adaptation, learning from adversity |
| Reflect on Experiences to Foster Growth | Use journaling, structured questioning, and emotional mapping | Increased self-awareness, wisdom from setbacks, ongoing growth |
Ready to Transform Setbacks Into Strength?
If you found inspiration in these key resilience-building exercises, you know that growth and adaptability take ongoing effort. Many people get stuck struggling to turn new skills like self-reflection, positive self-talk, or problem-solving into consistent habits. Are you looking for deeper guidance or real results—not just theory? Discover how Ashley Gustafson’s actionable workshops and coaching at NavigatingThroughQuicksand.com help you build genuine resilience in your life or team. Her sessions are packed with strategies to practice emotional regulation, set meaningful goals, and build authentic support systems—exactly the skills you just explored.
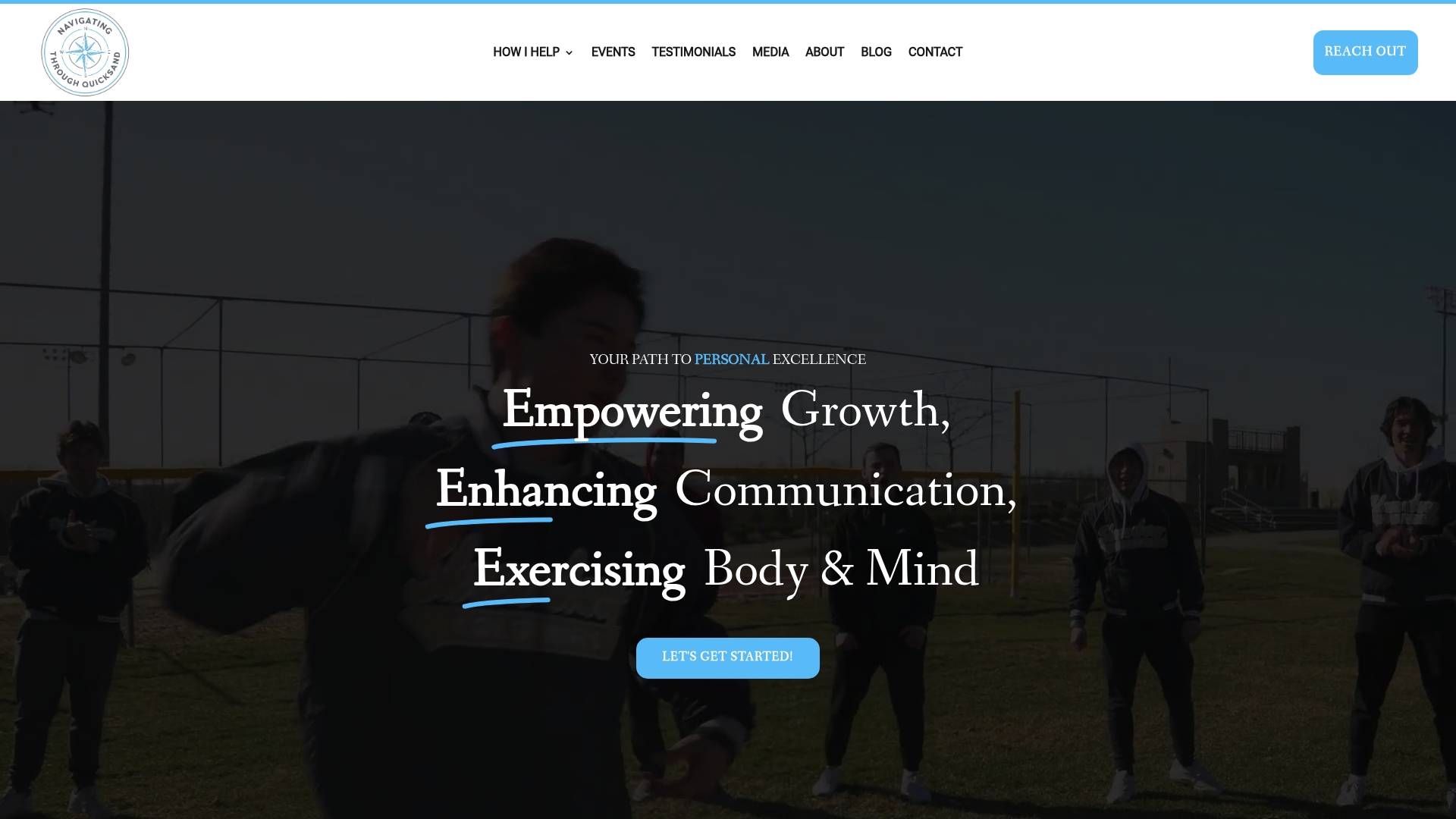
Opportunities to grow and thrive are waiting. Book a motivational speaking engagement or inquire about professional development workshops. Now is the time to strengthen your resilience and shape your future with expert support. Visit NavigatingThroughQuicksand.com to connect with Ashley and take the first step toward lasting change.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is resilience, and why is it important?
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from challenges and adapt to adverse circumstances. It plays a crucial role in managing stress, maintaining emotional well-being, and fostering personal growth through difficult experiences.
How can mindfulness and meditation help build resilience?
Mindfulness and meditation teach individuals to respond to stress with clarity and calmness, enhancing emotional awareness and improving coping mechanisms. Regular practice can lead to neurological changes that promote more adaptive responses to challenges.
What are SMART goals, and how can they aid in personal development?
SMART goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives that provide direction and motivation. They help individuals create actionable plans, making it easier to navigate through challenges and track progress in personal development.
How does positive self-talk contribute to resilience?
Positive self-talk transforms internal narratives from self-critical to supportive, influencing emotional responses and mental well-being. By reframing negative thoughts and practicing affirmations, individuals can cultivate resilience and maintain a constructive mindset during challenges.



